Introduction In the digital age, the importance of securing information has never been greater. Whether it’s personal data, business transactions, or government communications, encryption plays a critical role in protecting sensitive information. Two fundamental types of encryption techniques are symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. This article explores what they are, how they work, and their differences and use cases.
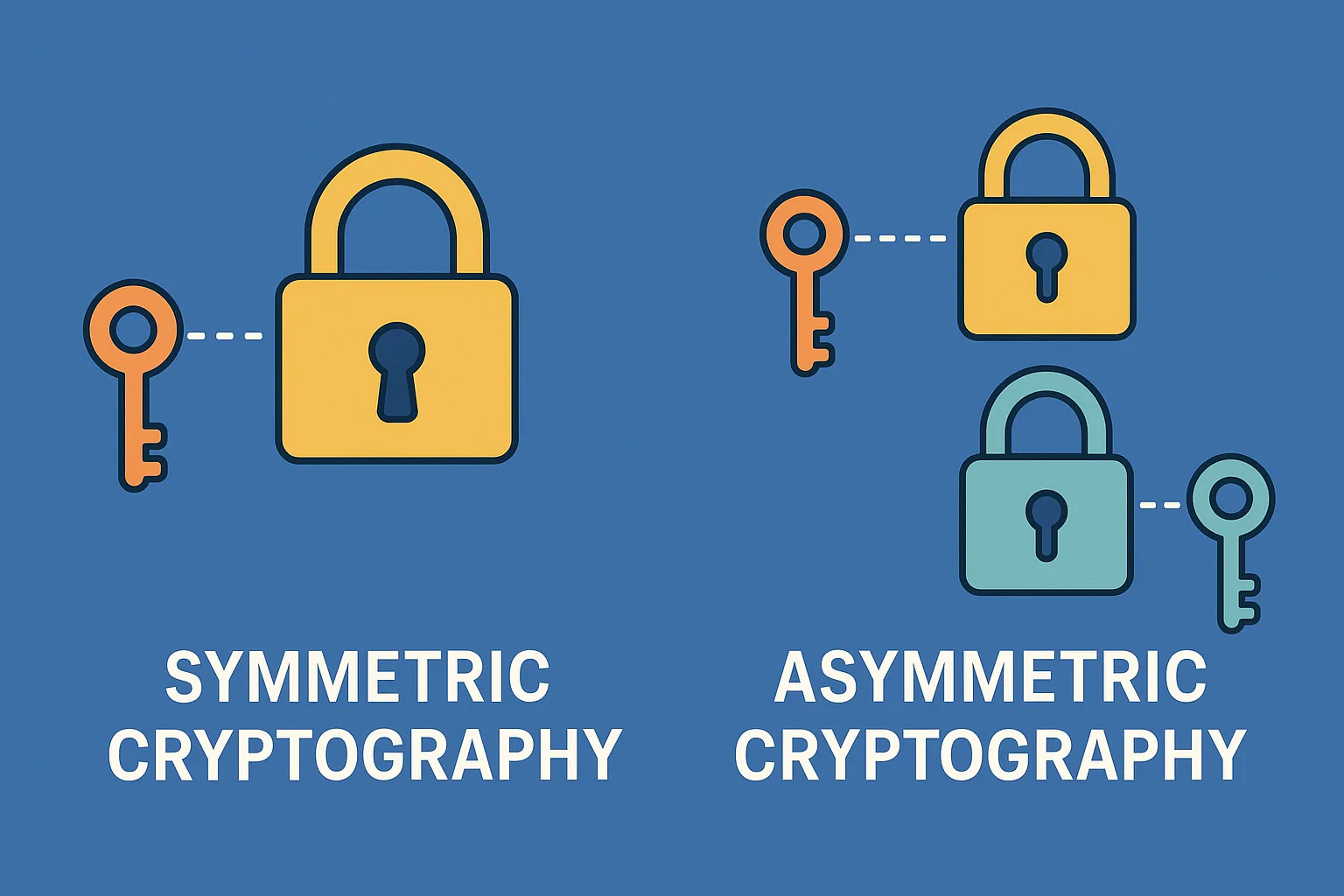
What is Symmetric Cryptography? Symmetric cryptography, also known as secret-key encryption, uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. This means that the same key must be shared and kept secret between the sender and the recipient.
How Symmetric Cryptography Works:
- A secret key is created and shared between parties.
- The sender encrypts the data using this key.
- The recipient uses the same key to decrypt the data.
Common Symmetric Algorithms:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- DES (Data Encryption Standard)
- Triple DES (3DES)
- Blowfish
Advantages of Symmetric Cryptography:
- Faster and more efficient for encrypting large volumes of data
- Simpler to implement with lower computational overhead
Disadvantages of Symmetric Cryptography:
- Key distribution is challenging and poses a security risk
- Both parties must securely share and manage the same key
What is Asymmetric Cryptography? Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public-key encryption, uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is shared openly, while the private key remains confidential.
How Asymmetric Cryptography Works:
- A key pair is generated: one public and one private.
- The public key is distributed to anyone who wants to send an encrypted message.
- The sender encrypts the message using the recipient’s public key.
- The recipient decrypts it using their private key.
Common Asymmetric Algorithms:
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
- ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
- DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)
Advantages of Asymmetric Cryptography:
- Eliminates the need to share private keys
- Provides digital signatures for authentication and non-repudiation
Disadvantages of Asymmetric Cryptography:
- Slower compared to symmetric encryption
- Higher computational demands
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Cryptography: Key Differences
| Feature | Symmetric Cryptography | Asymmetric Cryptography |
|---|---|---|
| Key Usage | Same key for both operations | Different keys for each |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Security | Dependent on key secrecy | More secure for key exchange |
| Use Case | Data-at-rest encryption | Secure communication, signatures |
Real-World Use Cases
- Symmetric: File encryption, VPNs, database encryption
- Asymmetric: SSL/TLS, digital signatures, email encryption
Conclusion Both symmetric and asymmetric cryptography play crucial roles in modern cybersecurity. Symmetric cryptography excels in speed and efficiency, while asymmetric cryptography provides better security for communication and key exchange. Often, systems employ a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of both methods to ensure robust data protection.
Understanding the nuances of symmetric and asymmetric cryptography helps IT professionals make informed decisions about securing systems, applications, and communications.